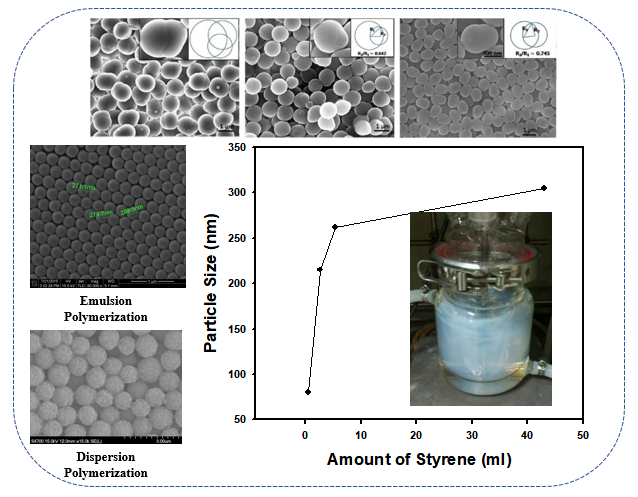
Synthesis of Functional Colloidal Particles and Self-assembly
Monodisperse particles can be synthesized as colloidal dispersion to prepare various self-assembled structures. In our laboratory, monodisperse particles are synthesized by emulsion and dispersion polymerization. Core-shell particles with catalytic property are also fabricated by wet-synthesis method. From the colloidal particles, we are developing structured colloidal materials with various functionalities. For instance, rapid fabrication of colloidal crystals for reflective display is underway.
Monodisperse particles can be synthesized as colloidal dispersion to prepare various self-assembled structures. In our laboratory, monodisperse particles are synthesized by emulsion and dispersion polymerization. Core-shell particles with catalytic property are also fabricated by wet-synthesis method. From the colloidal particles, we are developing structured colloidal materials with various functionalities. For instance, rapid fabrication of colloidal crystals for reflective display is underway.
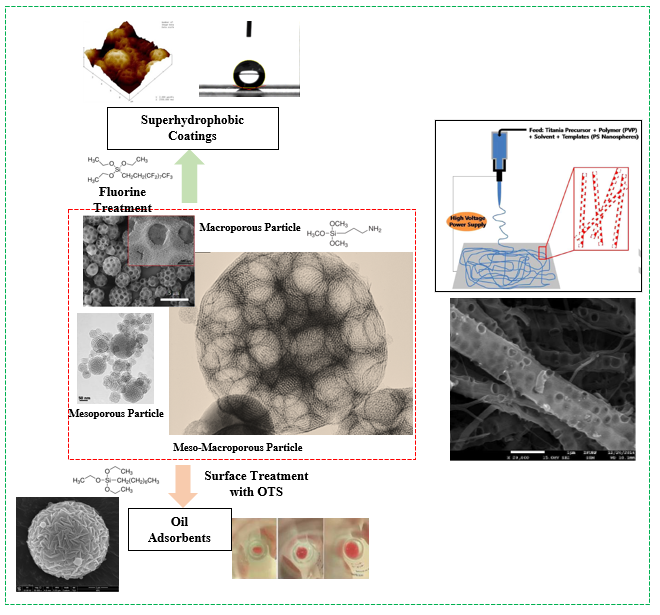
Fabrication and Application of Porous Materials
- Porous materials are defined as the structures with a number of pores, and they are classified with nanoporous, mesoporous, and macroporous materials according to the size of the pores. In our laboratory, various porous materials are synthesized by chemical reaction, spray drying, and electrospinning to apply sound absorber, thermal insulator, catalytic supports, adsorbents, and superhydrophobic coatings
- The extraction of source component like sodium silicate for porous materials is also underway from biowastes like rice husk.
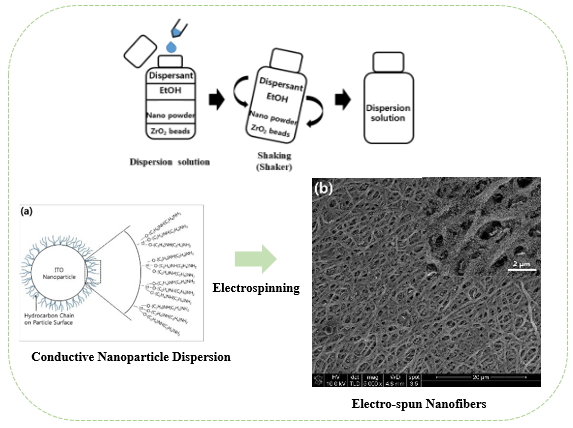
Synthesis of Functional Nanoparticles and Dispersion
- To prepare stable colloidal dispersion from nanoparticles, wet attrition process is required using high energy and proper dispersant. In our laboratory, we are preparing stable colloidal dispersions from functional nanoparticles to apply transparent and conductive films by electro-spinninig or spin coating.
- Synthesis of silica nanoparticles is underway from sodium silicate and carbon dioxide as reactants.
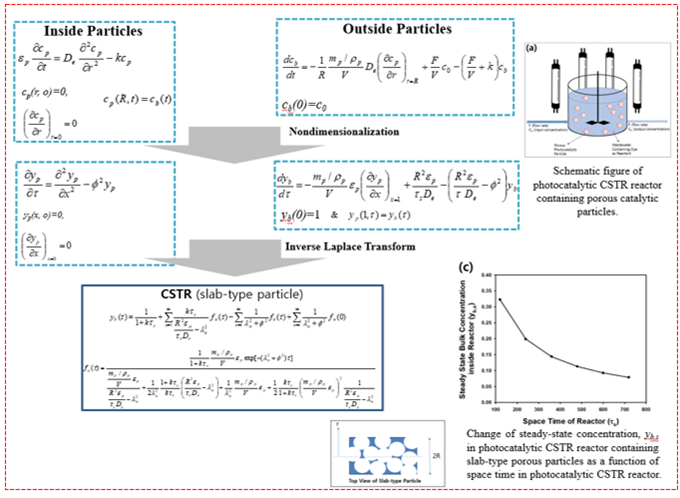
Modeling and Simulation of Biochemical Processes
- Reaction-diffusion equations are differential equations for interpretation of chemical reaction and diffusion phenomena, and they can be applied to analysis of chemical processes as well as spreading of viral infect to human body or city. In our laboratory, modeling of batch and continuous catalytic reactors are carried out by solving reaction-diffusion equations to compare the results with experimental data.
- Catalytic pellets and adsorbents with cylindrical or core-shell morphologies are studied for reaction and separation processes by analytical solutions and numerical methods using commercial softwares such as COMSOL or MATLAB. Analytical solutions are obtained by integral transform method, and approximate solutions are also studied by perturbation method.
- Modeling targets: core-shell pellets, core-shell adsorbents, immobilized enzyme reactors, photocatalytic reactors, CO2 absorption by emulsion system, heterogeneous reaction of solid and fluid, dynamic catalyst, spread of viral infection
Name: Prof. Young-Sang Cho
- Laboratory: Room 304, Building D, Tech University of Korea
- Tel : 031-8041-0612
- e-mail : yscho78@kpu.ac.kr
- Marquis Who‘s Who in the World (2015)
- Cover Papers in SCI journals
- Working with Group members from Vietnam
- We are recruiting Korean graduate students as well as foreign students from Overseas including Vietnam.- You can send e-mail to professor or group members
- Nguyen Hoai Han (han1219@tukorea.ac.kr)
Nguyen Thi Thu Hien (nghien2307@tukorea.ac.kr)
Recruiting Graduate Students

